The foreign exchange (forex) market is trendy today, thanks to increased connectivity and plentiful availability of online solutions. Because of the ease of access, many retail investors worldwide can participate in the world’s most liquid market.
You probably noticed that a few major currencies dominate the forex market. Moreover, you might know that more than 80% of the daily forex market volume consists of eight currencies.
The Canadian dollar is one of the majors
The Canadian dollar (CAD), also often referred to as the loonie, belongs to a class of the most traded currency pairs in the global forex market. Usually, traders refer to such pairs as major currency pairs or simply majors.
But more often than not, the market classifies only four currency pairs into the “majors club” – USDJPY, EURUSD, USDCHF, and GBPUSD. However, the USDCAD and other most actively traded pairs, such as NZDUSD and AUDUSD, sometimes meet the “majors” designation criteria.
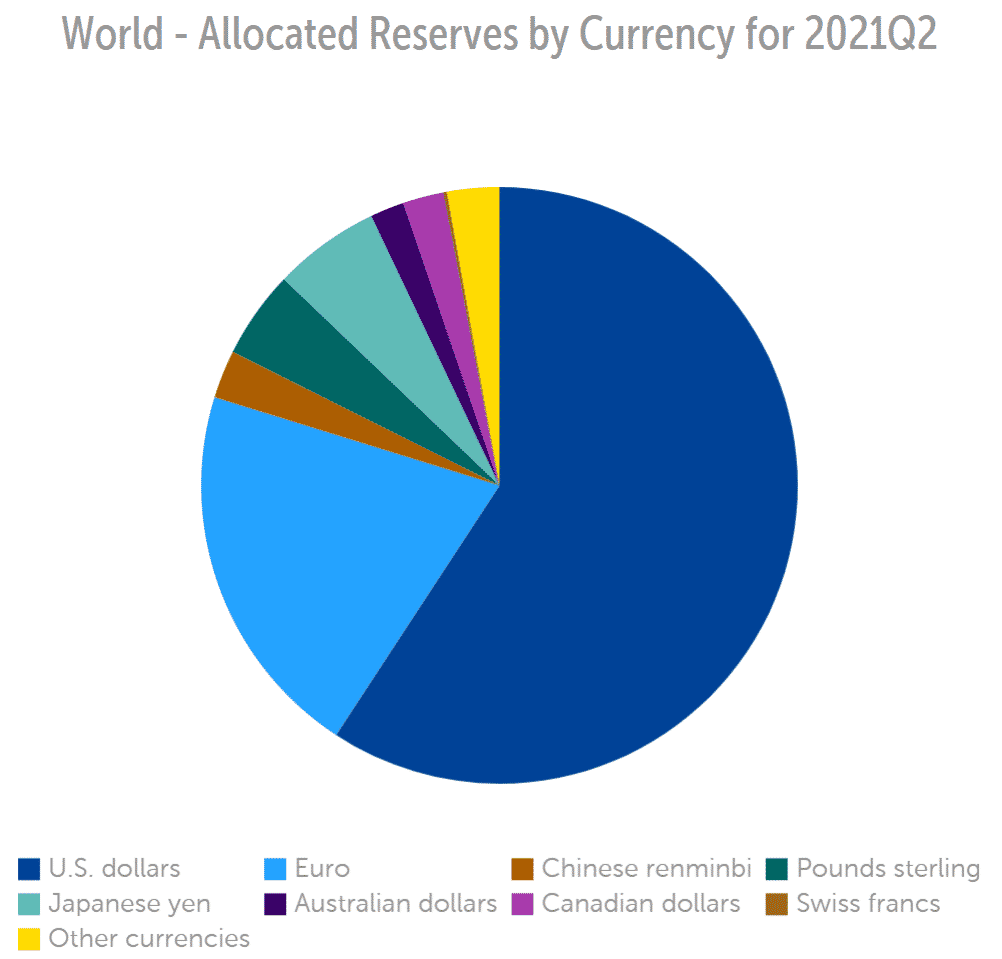
The loonie is also a major currency when viewed from the perspective of the IMF’s Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves (COFER). According to the latest COFER data, there were USD 265.93 billion claims in Canadian dollars in foreign reserves as of Q2 2021. It means 2.22% of the global foreign reserves are in CAD, six positions behind the US dollar. Other currencies in front of the loonie include the British pound, euro, Japanese yen, Chinese yuan, and the Swiss franc.
What should you think about when trading the Canadian dollar?
As with all the other currencies in the market, the loonie’s price action is a function of various factors. Usually, traders analyze the Canadian economy and other external indicators before buying or selling a currency pair, including the CAD.
Market analysis is a critical exercise in the life of a forex trader. It helps to uncover potential plays that could lead to massive returns. When trading the Canadian dollar, the following things should be part of the research.
Bank of Canada’s press conferences and interest rate decisions
In every economy, the central bank shoulders the colossal task of maintaining a stable financial system. The institution has particular tools at its disposal (often called monetary policy tools) to achieve the objective.
The Bank of Canada (BOC) is responsible for adjusting the country’s monetary policy to stabilize the loonie. Its most potent tool is the discount rate, also called the central bank rate.
Members of the institution’s monetary policy team meet every six weeks to set the central bank rate. The interest rate decision affects critical aspects of the economy, such as consumer borrowing and spending. By extension, the decision shifts the demand and supply scenarios for the CAD in the global forex market.
Sometimes the interest rate decision announcement itself is short on details. That is why traders track follow-up press conferences by any member of the monetary policy committee.
If the bank raises the discount rate, liquidity in the Canadian economy will decline. On the other hand, a high discount rate strengthens the CAD, and its value grows against rivals in the forex market.
Inflation data
In addition to managing the monetary policy, the BOC also tracks the economy’s inflation rate. Since inflation refers to the rate at which essential goods and services prices rise over time, the BOC’s mandate entails keeping the rate low and stable.
The BOC uses the discount rate to regulate inflation. For instance, it raises the discount rate to cool the economy during hyperinflation. However, a higher discount rate makes credit expensive, leading to lower consumption. On the flip side, the higher interest rate encourages consumers to save, strengthening the CAD in the forex market.
In conjunction with the BOC, Statistics Canada releases monthly inflation data in the form of the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Jobs data
The unemployment rate in the economy is also consequential for CAD’s performance in the forex market. For instance, traders use the jobs data to forecast the future strength of the economy.
When the jobs data comes in positive (an improvement in employment rate), traders’ sentiment regarding the loonie improves. Again, Statistics Canada is in charge of releasing jobs data once every month.
Also, it is worth noting that Canada’s employment data often comes out in parallel with the United States’ Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP). When released in tandem, it becomes challenging to trade the USDCAD pair using the jobs data – demand flows both ways during such periods, making it hard to predict the direction of the pair’s price action.
Oil prices
Canada has one of the best economic models globally: it has managed to keep the currency stable even when it relies more on commodity exports.
One of the country’s most crucial export commodities is oil. According to the latest data, the production and delivery of oil and its products account for about 10% of Canada’s GDP.
From the preceding, the link between Canada’s GDP growth and oil prices is vital. In other words, lower oil prices cause the demand for CAD to plunge, leading to lower exchange rates. However, the opposite is also true, where higher oil prices strengthen the loonie’s position in the market.
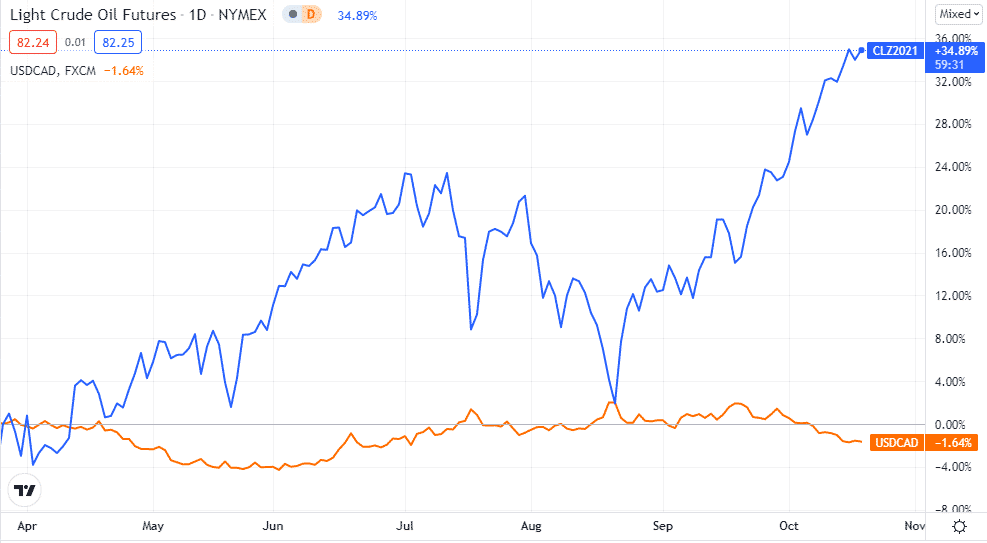
To illustrate, let’s look at the chart below. Between April and July 2021, crude oil futures (CLZ1) rose exponentially, whereas the USDCAD declined. A similar pattern is visible between August to present. This tells you that the price action for the USDCAD pair correlates inversely to oil prices.
Conclusion
Forex trading is an exciting venture when you know what you are up against and what things to consider. For example, the Canadian dollar is a favorite for many traders in the market for many reasons: its unique relationship with commodities and the ability to predict future price action based on factors like inflation data.
