Oil is one of the most important commodities at the global economy’s heart. Oil price changes impact the global economy more than anything, going by the number of sectors that rely on black gold. While prices are dependent on geopolitical development and economic events, one body is at the center of it all, OPEC.
Understanding OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries is the cartel that regulates oil prices worldwide. The body pools together some of the biggest oil-producing nations, allied to other op non-OPEC members. There is even a more powerful entity dubbed OPEC Plus.
The organization is tasked with regulating oil supply in the global markets. By controlling supply amid fluctuating demand, the cartel can influence prices significantly. With OPEC holding over 50% of oil supplies and 90% of reserves, it affirms its dominance in the oil business.
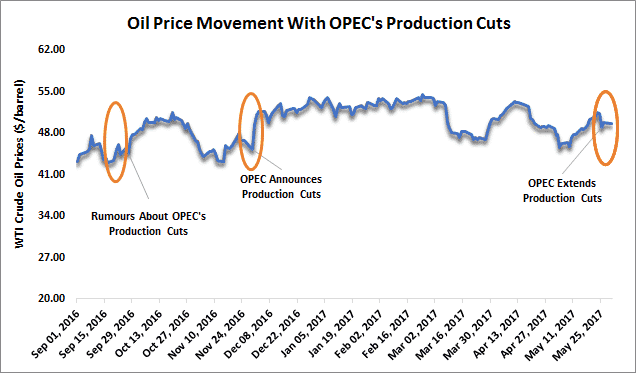
Whenever OPEC is unsatisfied with the prevailing oil prices, it institutes measures that alter the supply chain. By reducing supply and pushing for production cuts amid strong demand, the organization ends up achieving higher oil prices.
However, while no country ever wants to reduce its oil production given the prospects of reduced earnings from the oil business, OPEC has always struggled to meet its targets. In most cases, the member countries always want prices to continue increasing as they ramp up production.
OPEC impact on the forex market
OPEC’s decisions trigger wild swings in the forex market by influencing traders’ sentiments on various pairs. For starters, whenever OPEC Plus commits to cut oil supplies, extreme volatility in the currency market is often the result. Some currency pairs with exposure to the commodity tend to experience wild swings as market players react.
The Canadian dollar is one major currency always susceptible to OPEC decisions that alter the supply framework. Whenever OPEC cuts supplies resulting in an uptick in oil prices, the Canadian dollar strengthens against the other majors. Partly this is because oil is Canada’s biggest export, from where it generates most of its foreign reserves.
Similarly, oil prices tend to decrease whenever OPEC Plus refrains from cutting oil supplies or opts to increase supplies amid declining demand. Such decline is usually negative to the biggest oil-producing countries such as Canada. Consequently, the Canadian dollar tends to weaken against the majors whenever oil prices are edging lower.
The USDJPY is another pair susceptible to oil prices fluctuation given that Japan is a net importer of the commodity. Whenever oil prices increase on OPEC tightening supplies, Japan is often forced to spend more to purchase the much-needed commodity.
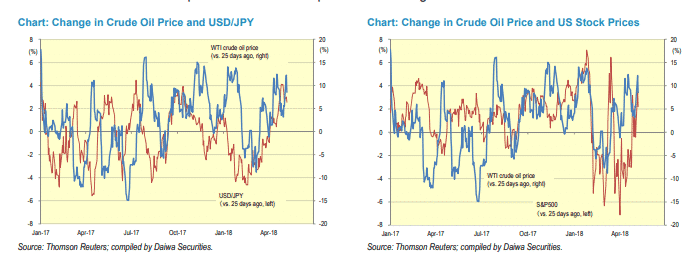
Increased outflows to support purchases of the commodity causes the yen to weaken against other major currencies. Consequently, in most cases, USDJPY will turn bullish, edging higher as the yen weakens on rising oil prices.
Oil and US dollar correlation
Crude oil prices are normally quoted in dollars. Conversely, any fluctuation in the greenback strength is known to affect oil prices. Whenever the US dollar strengthens in the market, oil prices decline. Similarly, oil prices edge higher whenever the greenback weakens, thus the inverse correlation between the two.
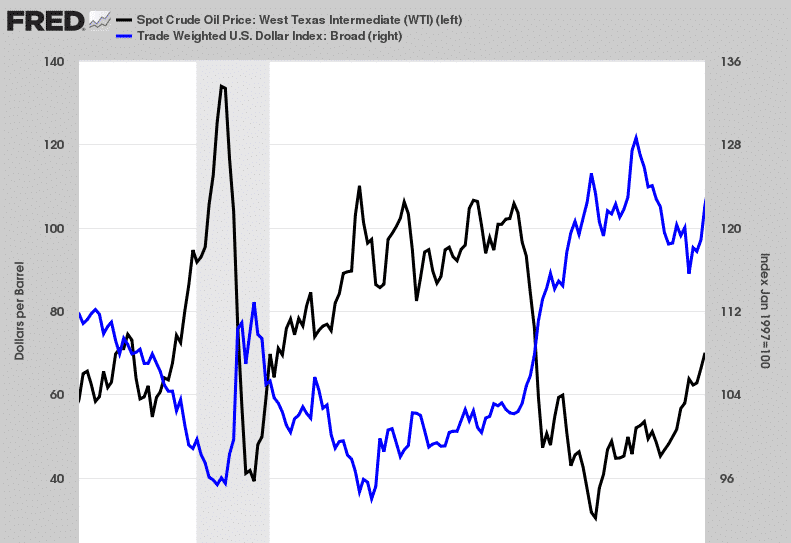
The inverse correlation exists because one needs fewer dollars to buy oil whenever the dollar strengthens. Likewise, whenever the dollar weakens, one would need more money to buy oil. For the longest time, the US was a net importer of the commodity. However, since 2011, the country has become a net exporter thanks to horizontal drilling and fracking successes.
The US becoming a net exporter has resulted in the US dollar and oil price inverse relation becoming more unstable. In addition, the US has started challenging OPEC decisions triggering wild swings in the market.
For instance, whenever OPEC fails to ramp up production to meet demand as a way of keeping prices higher, the US tends to release some of its oil reserves into the market. The flooding of the market with more supplies acts as a counter to higher prices. The result is the weakening of currencies susceptible to oil prices, such as the Russian ruble, Canadian dollar and the Brazilian real.
Oil prices vs. stocks
OPEC decisions also go a long way in influencing activities in the stock market directly and often indirectly. Any decision that results in an uptick in oil prices often causes most input costs to increase significantly. As companies spend most of their capital to cater to the increased costs, profit margins shrink.
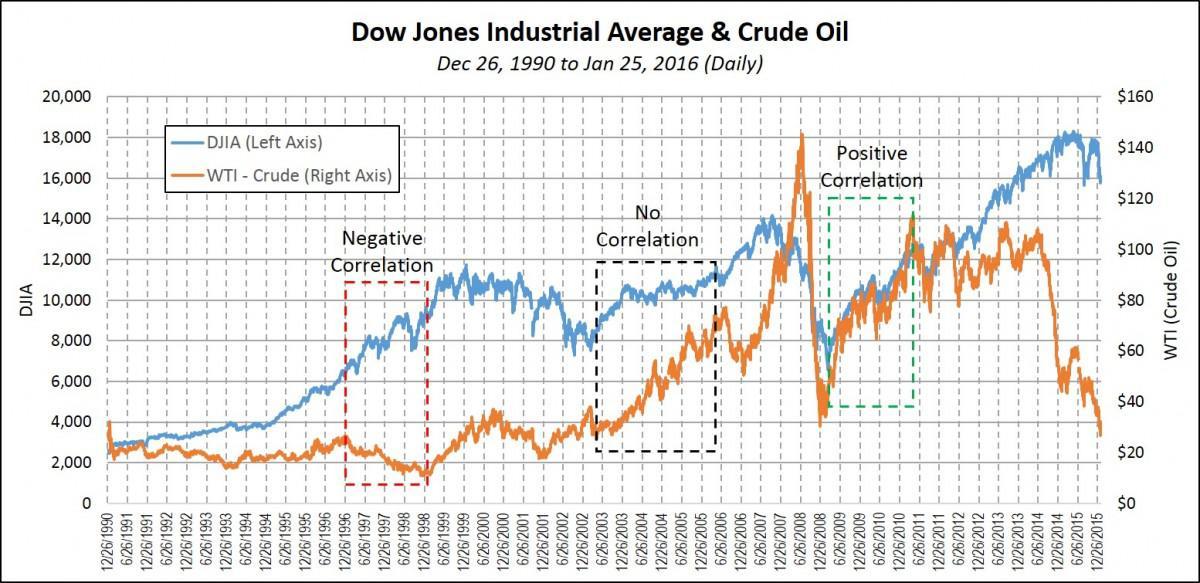
In return, such stocks tend to underperform on coming under pressure from investors. Increased oil prices also forces consumers to spend more on gasoline. Therefore, they are left with little to spend on the products and services offered by most companies.
Consequently, such companies and businesses end up with a shrinking revenue base, which often ends up affecting their performance in the stock market.
Oil prices vs. inflation
Whenever OPEC refrains from ramping up production among member countries, oil prices tend to increase on demand remaining the same or edging higher. The net effect, in this case, is a spike in inflation. Subsequently, the prices of goods in net importer countries tend to increase.
The US is one country that has seen prices of goods edge higher on oil prices increase significantly. A spike in Inflation often calls central banks into action. For instance, the Federal Reserve has started tightening monetary policy after inflation rose to 40-year highs of 7%.
Aggressive monetary tightening to curtail runaway inflation often causes the dollar to strengthen against the majors. In this case, the GBPUSD and EURUSD often come under pressure edging lower in the currency market.
Final thoughts
OPEC is the cartel that impacts oil prices by being in control of more than 50% of the oil that hits the market. Its decisions go a long way in affecting oil prices which in return affects the amount of money that net exporters such as Canada make conversely affect Canadian dollar strength in the market.
