Foreign exchange is a market that represents not only the demand and supply dynamics of the currency but also the economy of a country. When it comes to markets of this scope, nearly all of them are inter-connected. We know that the price of a commodity would impact a nation that is a major importer or exporter of it. Similarly, we know that inflation and economic growth affect the forex pair related to the country.
Bond market prices also indicate both the health of the economy and confidence in the currency. The bond market is the largest market in the world and is estimated to be $120 trillion globally! With high stakes, bond market participants are thought to be the smartest people. Hence movements in bond markets are tracked carefully to assess the direction of other markets.
What are bond yields?
Pricing in the bond market is slightly different where the bonds are quoted by their ‘yields’ and not their prices. Bonds typically return the principal at the end of their term and a periodic coupon. So the return is not just from the change in the price of the bond and also the coupon.
The combination of these two returns is known as yield. So, for example, a bond with a $100 principal and 6% coupon maturing next year is trading at $98, then the yield will be 8%. As you must have noticed, the lower the bond price, the higher the yield will be. So these 2 have an inverse relationship.
So how should one assess the health of an economy from bond yields?
Bond yields follow the simple rule of high-risk, high reward. If a country’s economy is weak or falling, investors will see a higher risk of investing. Consequently, they will demand higher returns which are reflected in the high bond yields of that country. So if a country’s bond yields move higher, it means that the country’s economy is seeing some issues. Similarly, if the bond yields fall, then it means the country’s economy is strengthening or growing fast.
The important thing to remember here is that bond yields start reflecting the state of the economy even before the official economic numbers are released. This is because bond traders are constantly monitoring high-frequency indicators and assessing the ground situation.
Hence, their trades are also based on how the economy will emerge in the next few months rather than on the already released economic data. This indicates that bond yields are leading indicators.
Forex pairs and bond yield spreads
Now that we understand what bond yields are and what they represent let’s try to understand the concept in the context of FX trading. While bond yields indicate the strength of its respective economy, in FX trading, we always deal with currency pairs. So in order to assess the direction of the forex pair’s price, we also need to know about both currencies. Similarly, when using bond yields, we need to look at the ‘yield spread’ rather than the individual yields of the countries.
The yield spread is nothing but the difference between the yields of the government bonds of 2 countries. Since bonds are of different tenures, such as one year, three years, five years, ten years, and so on, the 10-year bonds are chosen as benchmarks. So, for example, if someone is talking about the yield spread for the UK and the US, they would most probably mean the difference in yields of their 10-year sovereign bonds.
Secondly, the convention is that the lower yield is subtracted from the higher yield. For example, the US 10 year yield at the time of writing is 1.5%, while UK 10 year yield is 0.76%. So the yield spread between these two is defined as the US 10 year yield minus the UK 10 year yield, which is 0.74%.
Then we go on to track this spread rather than the individual yields. If the yield spread increases, it means that the prospects of the US economy are better than those of the UK economy. This might be an indicator for the GBPUSD price to fall.
Understanding yield arbitrage impact on FX trading
Another way to interpret the impact of yield spread on forex trading is from the lens of yield arbitrage. There are cases where the difference between the yields of 2 countries is more than 1% or even 4% to 5% in the case of emerging markets. In such cases, traders set up an arbitrage trade.
They borrow money in a lower-yielding currency, say USD, and buy a high-yielding currency, for example, INR, which yields 6%. So the traders earn nearly 5% of yield if the underlying forex pair of USDINR remains stable.
So when the yield spreads widen, it becomes an attractive yield arbitrage trade. So more traders will borrow USD and buy INR, which in turn will push down the USDINR pair. This is because there will be inflows in INR which will strengthen the currency.
So above, we saw two important ways in which yield spreads affect forex trades. What’s interesting about yield spreads is their impact on forex trading is only because of the actions taken by market participants. The correlation doesn’t rely solely on fundamental factors but also on how traders react to it. As a result, the correlation and impact are much stronger as compared to other indicators.
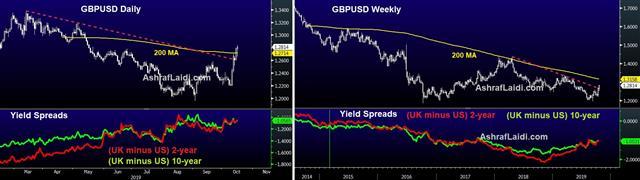
It is important to remember, though, that these play out on a relatively long term by virtue of being macro indicators, as seen above. So while developing a trading strategy using yield spreads, traders should consider long-term intervals. Weekly data points will yield better results rather than using daily data points.
One must also keep in mind that yield spreads are just one among the many factors that affect forex trades. So it is better to use yield spread in the combination of other technical and fundamental indicators in order to achieve superior returns.
